Videos Explaining Difference in Conic and Mercator Maps
Map projections are used by mapmakers for navigation travel roads and weather. Central Cylindrical Silhouette Map c Tobias Jung Mercator Silhouette Map c Tobias Jung.

Objectives Differentiate Between Mercator Robinson And Conic Map Projections 4 Calculate Time And Date In Different Time Zones Ppt Video Online Download
Give each group one copy of the 3-page worksheet Map to Globe.

. Mercator is used for navigation or maps of equatorial regions. Click on projections name to hide it. Centred on 140 East and the Equator.
Red circles on the map confirm that map scale is equal along both standard parallels. Mercators projection shows that Greenland is the size of Africa that Alaska is larger than Brazil and that. Jun 26 2019 0945 AM.
For the normal aspect the apex of the cone lies on the polar axis of the EarthIf the cone touches the Earth at just one particular parallel of latitude it is called tangentIf made smaller the cone will intersect the Earth twice in which case it is called secant. Map projections are based on an arrangement of parallels and meridians that represent a geographic coordinate system Chang 2012. Yes Mercator Robinson and conic projections differ because Mercator Robinson is not true its Mercator projection.
A conic projection is derived from the projection of the globe onto a cone placed over it. An additional feature of this projection is that all local shapes are accurate and correctly defined at infinitesimal scale. Unlike conic projections the meridian is not constrained to be a straight line.
Conceptual model of a Lambert Conformal Conic map projection left and the resulting map right. See answer 1 Best Answer. As Mercators projection moves away from the equator the representation of the Earths surface is distorted.
2-D to 3-D Models scissors and transparent tape. Conic Map Projections. This distortion makes the shapes found at the poles look bigger than they really are.
Many world maps still use Mercator projection today. A map projection is defined as a tool that transforms the Earths surface into a flat plane that can be shown on paper andor digital maps. Conic projections are a map projections of.
Mercator projections are the grid is rectangular and lines of latitude and longitude are all parallel. Have groups study these versions of the globe. The maps are not constrained to rectangles or discs.
First map has standard Parallels at 30 and 60 South and the second has standard Parallels at 30 and 60 North. A method of projecting maps of parts of the earths spherical surface on a surrounding cone which is then flattened to a plane surface having concentric circles as parallels of latitude and radiating lines from the apex as meridians. Likewise what is a conic projection.
Examples of pseudoconic projections include bonne which is an equal-area map projection. The two thick red lines marking the intersections of the globe and the projection surface the cone correspond with two standard parallels on the map. Click to see full answer.
If youre thinking of a world map youre probably thinking about the Mercator projection which flattens the globe into a rectangular presentation and in the process severely. Nov 12 2018 1156 AM. The Difference Between The Mercator Projection And Real Geographic Sizes Visualized.
Secondly conic map projections include the equidistant conic projection the Lambert conformal conic and Albers conic. Map projections used by cartographers are grouped into two major. The Peters projection map uses a rectangular coordinate system that shows parallel lines of latitude and longitude.
For example on a globe Greenland is fairly small but in a Mercator map Greenland is stretched out to look almost as big the United States. The Web Mercator variant of the projection. Pseudoconic Projections are projections with parallels which are circular arcs with common central points.
Mercator is a conformal cylindrical map projection that was originally created to display accurate compass bearings for sea travel. Divide students into small groups of three. It was presented by Gerardus Mercator in 1569.
Any straight line between two points is a true line of constant direction but not usually the shortest distance between the two. These maps are defined by the cone constant which dictates the angular distance between meridians. Explore map projections and the role of cartographers and learn about Mercator gnomonic and conic map projections.
Tell students they will next test the reverse changing from a flat map to 3-D. In a Mercator projection all compass directions are straight lines but a curved line is the shortest distance between the two points. The Lambert Conformal Conic is the preferred projection for regional maps in.
1- Distortion of the Earths surface. Click here or on the image to toggle projections. Have students create globes from different maps.
In reality the Mercator map was never intended to be used as a wall map and by the time Peters started complaining about it the Mercator map was well on its way out of fashion anyway. These meridians are equidistant and straight lines which converge in locations along the projection.
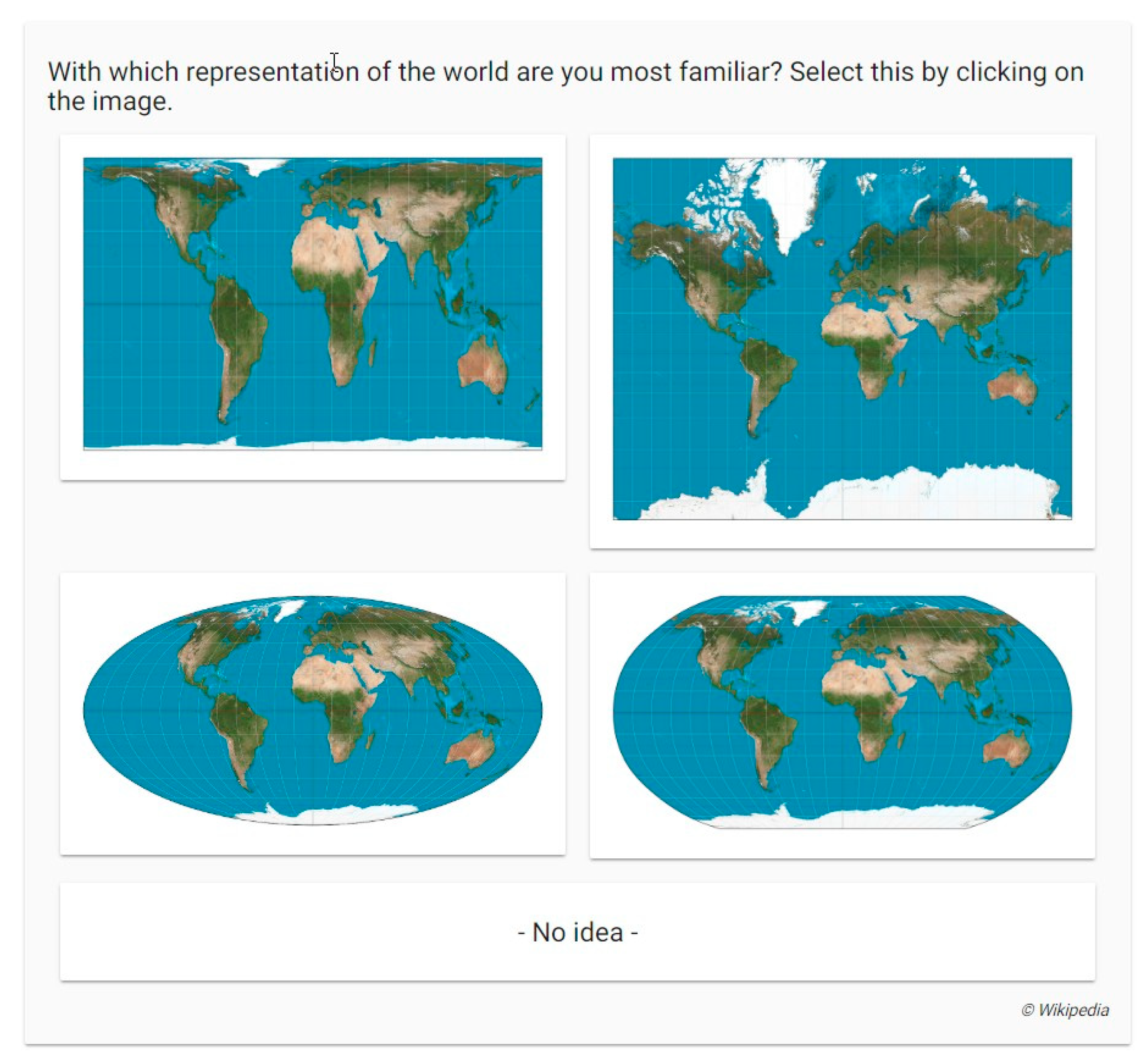
Ijgi Free Full Text The Influence Of Map Projections On People S Global Scale Cognitive Map A Worldwide Study Html

Map Projections Mercator Gnomonic Conic Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
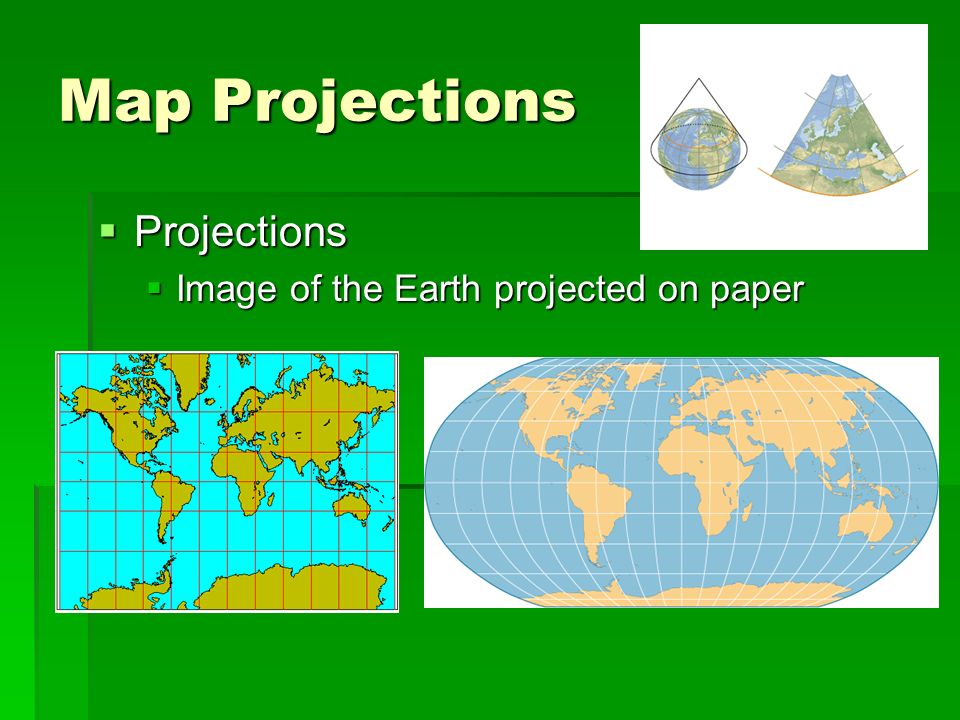
Objectives Differentiate Between Mercator Robinson And Conic Map Projections 4 Calculate Time And Date In Different Time Zones Ppt Video Online Download

Get To Know A Projection Lambert Conformal Conic Wired Science Map Celestial Map World Map
Comments
Post a Comment